How To choose the right database for your application ?
Introduction
As today,
DBaas provides 3 types of databases:
- A relational database based on Postgresql Single Server
- A non relational database based on CosmoDB with a MongoDB API
- An indexing database based on Opensearch.
The decision between these 3 offers will depend largely on the workloads you plan to support and the structure and amount of data. owever, you should also consider combining the databases regarding your application data
Guidelines
The following table provides a few general guidelines you might consider when weighing one type against the other.
| Consider relational database when… | Consider non relational database when… |
|---|---|
| Your data is highly structured, and that structure doesn’t change frequently | You’re working with large amounts of unstructured or semi-structured data that doesn’t fit the relational model |
| You support transaction-oriented systems such as accounting or financial applications | You require the flexibility of a dynamic schema or want more choice over the data model |
| You require a high degree of data integrity and security | You require a database system that can be scaled horizontally |
| You routinely perform complex queries, including ad hoc requests | You want to streamline development and avoid the overhead of a more structured approach |
Is my data structured or unstructured ?
To go further, you may not know if your data is structured or unstructured , the following table provides you some specificities:
| Structured data | Unstructured data | |
|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | Pre-defined data model Clearly defined Quantitative data Easy to access Easy to analyze | No pre-defined data model Is not clearly defined Qualitative data Difficult to access Difficult to analyze |
| Analysis Methods | Regression Classification Clustering | Data mining Natural language processing Vector search |
| Examples | Names Dates Addresses Credit card numbers Geographic position Product IDs Billing Data Financial transactions | Sensor data Text files Photos, audios and videos Weather data landforms Military movements Reports |
Common patterns
In order to help you in your decision, you should consider a modern application as a set of services (or micro services) with their own set of unstructured and structured data. More often than not industries need to leverage both data types to improve the efficiencies of their services.
Example
As an example, the following schema puts into practice DBAAS offers with the bookstore API
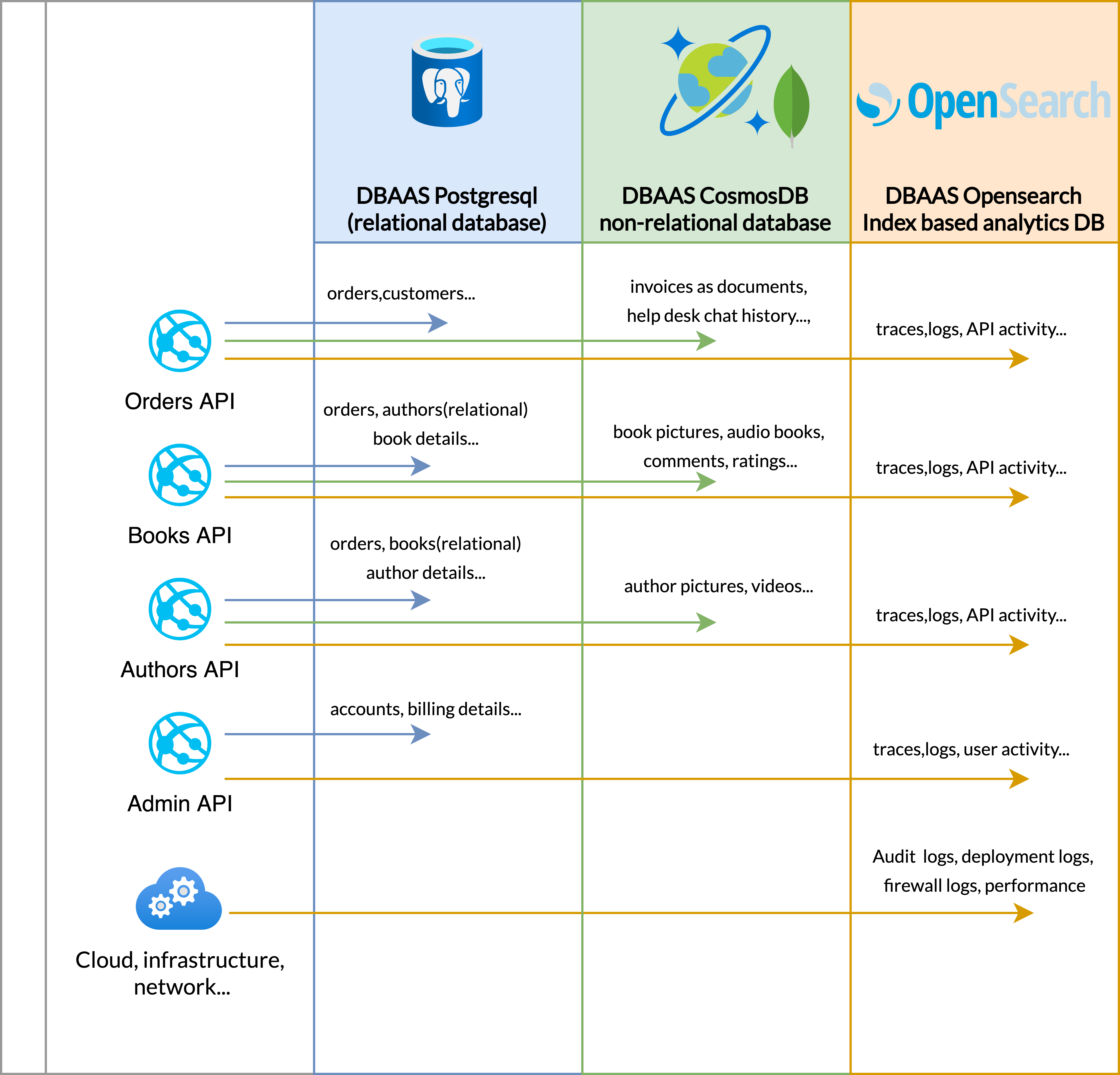
Motivation details
- Orders, customers, books and authors are stored in PostgreSQL
- Data model is structured during the application design with clear relations and the structure doesn't change frequently
- Data integrity and security is critical
- It supports complex queries and fits into a standard data structure with rows and columns
- It supports ACID transactions and locking mechanisms to ensure data integrity and business continuity
- Documents, medias, comments, and chat history are stored in CosmosDB
- Amount of data is hard to predict
- Data model is variable, complex to structure and sustain
- Traces, logs, API activity, events are stored in Opensearch
- It supports indexing based on patterns
- It supports analytics and text search
In addition, sending underlying system logs (Example: Network, firewall, access logs... ) in DBAAS Opensearch enable correlations and enhance end-to-end analysis