User & technical access management (RBAC)
Context
In most cases, a database is coupled with another system. Technical accounts are used to perform the authentication between the systems. It's very important to use minimum privileges when you access to the database to limit the impact of a technical account theft.
However, an administrator must need to full access to the database. That's why we provide nominative access to operate the DBaas using Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA).
DBaas Postgresql
DBaas postgresql relies on Azure Database for PostGresSQL Single Server. Authentication and authorization leverage features available on the service and already in GA.
1.1. Authentication for dbaas postgresql
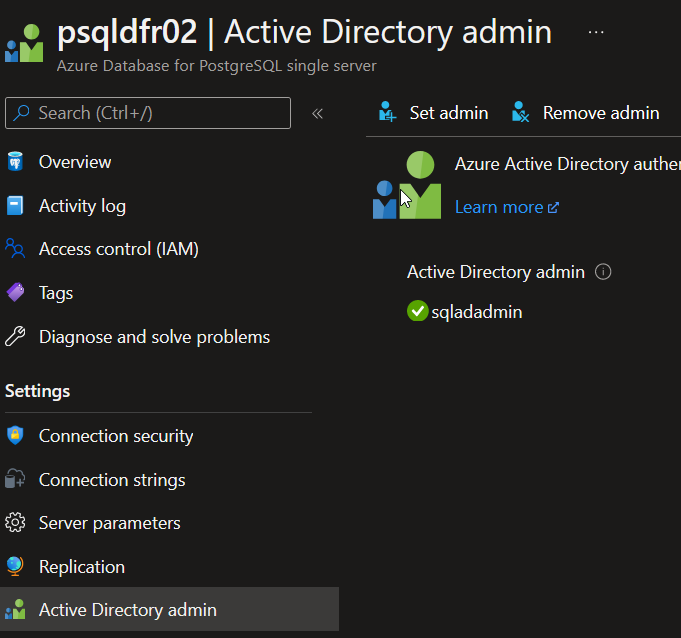
Azure Database for PostGresSQL Single Server integrates with Azure AD with.
The configuration relies on adding a dedicated Azure AD principal as an Active Directory Admin.
Note: While the name might imply a reference to Active Directory Domain service, it does refers to Azure Active Directroy
1.2. Authorization for dbaas postgresql
The specified service principal is granted postgres admin credentials and can managed authorization inside the postgresql control plane, or add databases. It is used to create 2 additionals role inside the dbaas postgresql instance:
- A dev role, following the name pattern
dbaas-xxx-pg-dev - A devops role, following the name pattern
dbaas-xxx-pg-devops
the xxx string refers to the tenancy and instance of the dbaas postgresql
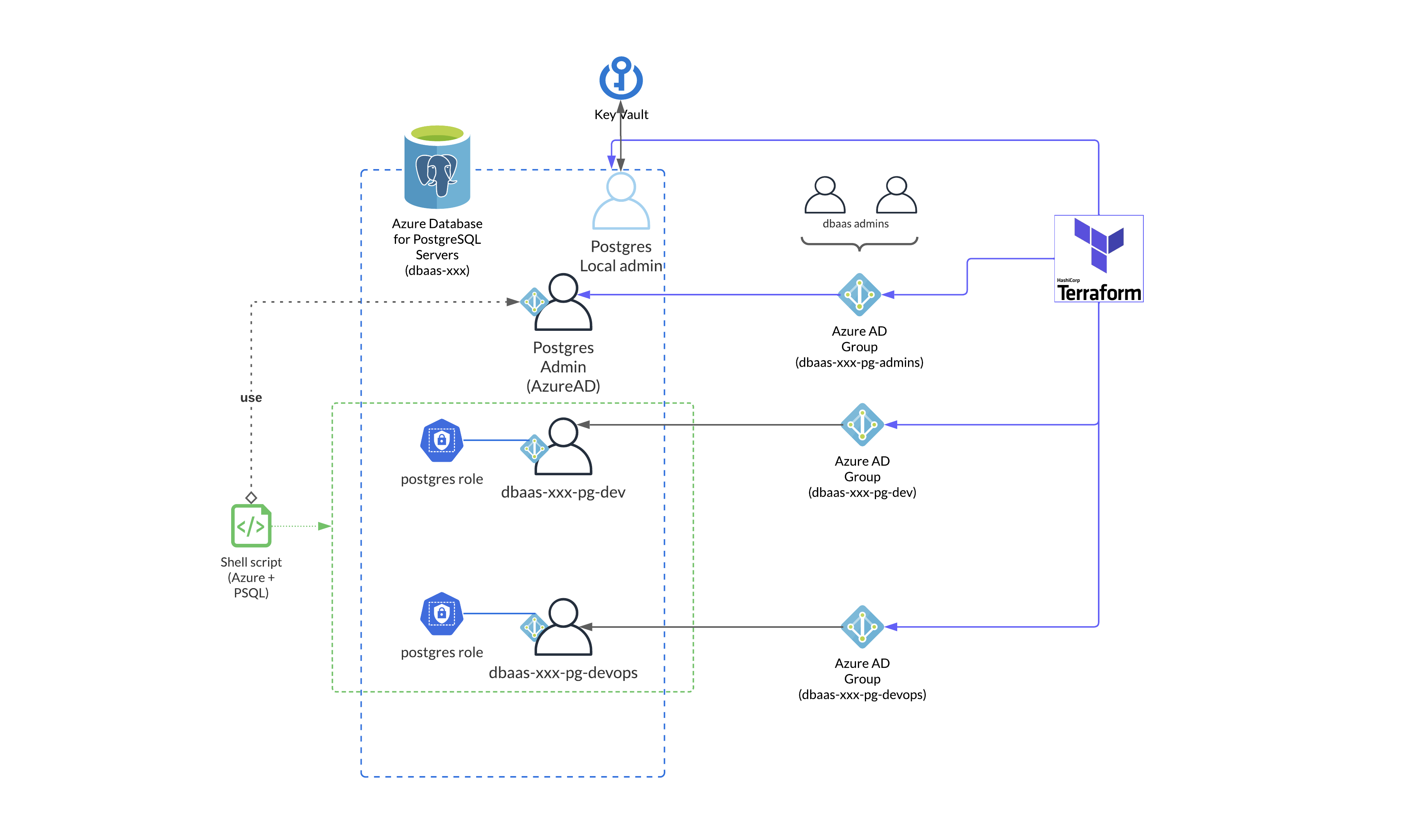
Apart from this Azure AD Admin, no other access is granted on the Azure control plane of the dbaas postgresql instance
DBaas CosmoDB
DBaas nosql relies on Cosmos DB and specifically Cosmos DB with MongoDB API.
Authentication and authorization are considered from both Azure Control plane and DBaas Data plane contrary to the dbaas postgresql for which the end user only has to consider the dbaas data plane.
2.1. Authentication for dbaas nosql
Because it is largely integrated to the Azure portal, authentication to dbaas nosql relies on Azure Active Directory.
To gain access to the dbaas nosql instance in Azure, users are granted 2 roles:
- Built-in role Cosmos DB Account Reader Role:
{
"assignableScopes": [
"/"
],
"description": "Can read Azure Cosmos DB Accounts data",
"id": "/subscriptions/{subscriptionId}/providers/Microsoft.Authorization/roleDefinitions/fbdf93bf-df7d-467e-a4d2-9458aa1360c8",
"name": "fbdf93bf-df7d-467e-a4d2-9458aa1360c8",
"permissions": [
{
"actions": [
"Microsoft.Authorization/*/read",
"Microsoft.DocumentDB/*/read",
"Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/readonlykeys/action",
"Microsoft.Insights/MetricDefinitions/read",
"Microsoft.Insights/Metrics/read",
"Microsoft.Resources/subscriptions/resourceGroups/read",
"Microsoft.Support/*"
],
"notActions": [],
"dataActions": [],
"notDataActions": []
}
],
"roleName": "Cosmos DB Account Reader Role",
"roleType": "BuiltInRole",
"type": "Microsoft.Authorization/roleDefinitions"
}
This role grant a reader access to the dbaas nosql account and also allow to get the read-only key
- Custom role Dbaas-Nosql-GetKeys:
{
"id": "/subscriptions/{subscriptionId}/providers/Microsoft.Authorization/roleDefinitions/{customroleguid}",
"properties": {
"roleName": "Dbaas-Nosql-GetKeys",
"description": "A custom role that, added with built'in role Cosmos DB Account Reader Role allows to get the write keys of cosmosdb account and define a connection on a compatible client",
"assignableScopes": [
"/subscriptions/{subscriptionId}"
],
"permissions": [
{
"actions": [
"Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/listKeys/action"
],
"notActions": [],
"dataActions": [],
"notDataActions": []
}
]
}
}
This role add the capability to get the write key
2.2. Authorization for dbaas nosql
As introduced in the previous part, authorization in dbaas nosql is relying on access key.
When granted Cosmos DB Account Reader Role, a user can get the read-only access key and thus read data in dbaas nosql.
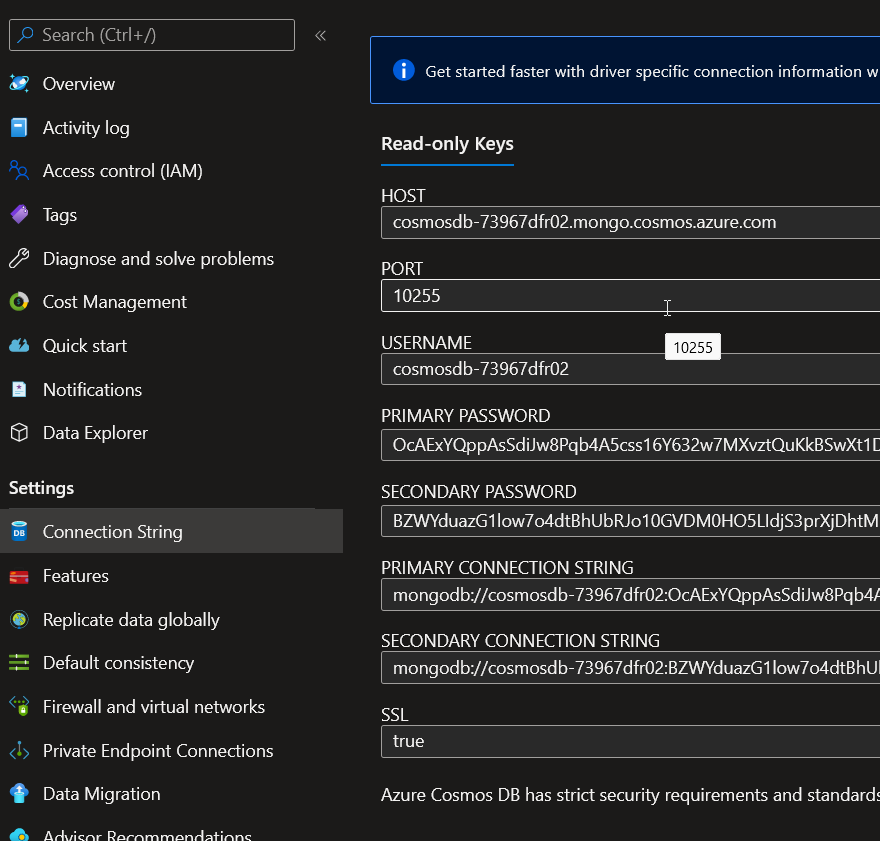
Viewing read key for a dbaas nosql mongodb api
Adding the Custom role Dbaas-Nosql-GetKeys, a user can get access to the write key:
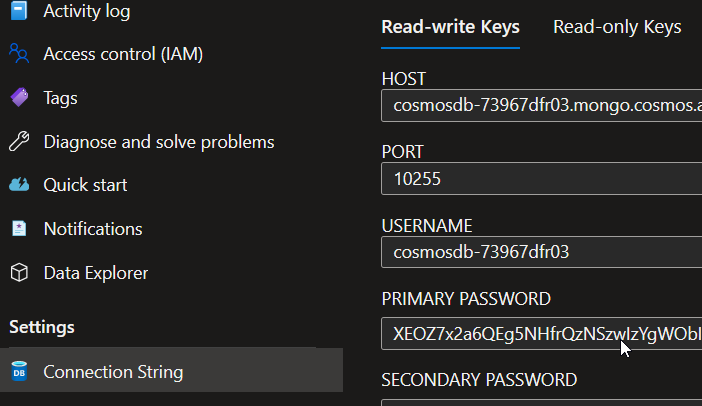
Viewing read-write key for a dbaas nosql mongodb api
Note: With those roles added, it is not possible to use the data explorer in the portal to write in the databases. Only PUT operations through the API with the read-write key can.
Granting read and write access to the embedded data explorer requires additional custom roles.
2.3 Write access with data explorer for dbass nosql mongodb api
The following custom role is require for write access on dbaas nosql with mongodb api:
{
"id": "/subscriptions/{subscriptionId}/providers/Microsoft.Authorization/roleDefinitions/{customroleguid}",
"properties": {
"roleName": "Dbaas-nosql-MongoDBWrite",
"description": "A custom role that, added with built'in role Cosmos DB Account Reader Role allows to interact with Data in cosmos db account with mongodb api in the Data explorer",
"assignableScopes": [
"/subscriptions/{subscriptionId}"
],
"permissions": [
{
"actions": [
"Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/mongodbDatabases/*"
],
"notActions": [],
"dataActions": [],
"notDataActions": []
}
]
}
}
In total, it grants the following 28 authorizations:
| API Action type | Permissions | description | API path |
|---|---|---|---|
| Write | Write MongoDB database | Create a MongoDB database | Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/mongodbDatabases/write |
| Read | Read MongoDB database(s) | Read a MongoDB database or list all the MongoDB databases. | Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/mongodbDatabases/read |
| Delete | Delete MongoDB database | Delete a MongoDB database. | Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/mongodbDatabases/delete |
| Write | Write MongoDB collection | Create or update a MongoDB collection. | Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/mongodbDatabases/collections/write |
| Read | Read MongoDB collection(s) | Read a MongoDB collection or list all the MongoDB collections. | Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/mongodbDatabases/collections/read |
| Delete | Delete MongoDB collection | Delete a MongoDB collection. | Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/mongodbDatabases/collections/delete |
| Other | Merge the physical partitions of a MongoDB collection | Merge the physical partitions of a MongoDB collection | Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/mongodbDatabases/collections/partitionMerge/action |
| Read | Read operation results | Read status of the asynchronous operation. | Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/mongodbDatabases/collections/operationResults/read |
| Read | Read operation results | Read status of the asynchronous operation. | Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/mongodbDatabases/collections/partitionMerge/operationResults/read |
| Write | Write MongoDB collection throughput | Update a MongoDB collection throughput. | Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/mongodbDatabases/collections/throughputSettings/write |
| Read | Read MongoDB collection throughput | Read a MongoDB collection throughput. | Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/mongodbDatabases/collections/throughputSettings/read |
| Other | Migrate MongoDB collection offer to autoscale | Migrate MongoDB collection offer to autoscale. | Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/mongodbDatabases/collections/throughputSettings/migrateToAutoscale/action |
| Other | Migrate MongoDB collection offer to to manual throughput | Migrate MongoDB collection offer to to manual throughput. | Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/mongodbDatabases/collections/throughputSettings/migrateToManualThroughput/action |
| Other | Redistribute throughput for the specified physical partitions of the MongoDB collection. | Redistribute throughput for the specified physical partitions of the MongoDB collection. | Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/mongodbDatabases/collections/throughputSettings/redistributeThroughput/action |
| Other | Retrieve throughput for the specified physical partitions of the MongoDB collection. | Retrieve throughput for the specified physical partitions of the MongoDB collection. | Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/mongodbDatabases/collections/throughputSettings/retrieveThroughputDistribution/action |
| Read | Read operation results | Read status of the asynchronous operation. | Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/mongodbDatabases/collections/throughputSettings/operationResults/read |
| Read | Read operation results | Read status of the asynchronous operation. | Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/mongodbDatabases/collections/throughputSettings/migrateToAutoscale/operationResults/read |
| Read | Read operation results | Read status of the asynchronous operation. | Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/mongodbDatabases/collections/throughputSettings/migrateToManualscale/operationResults/read |
| Read | Read operation results | Read status of the asynchronous operation. | Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/mongodbDatabases/operationResults/read |
| Write | Write MongoDB database throughput | Update a MongoDB database throughput. | Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/mongodbDatabases/throughputSettings/write |
| Read | Read MongoDB database throughput | Read a MongoDB database throughput. | Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/mongodbDatabases/throughputSettings/read |
| Other | Migrate MongoDB database offer to autoscale | Migrate MongoDB database offer to autoscale. | Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/mongodbDatabases/throughputSettings/migrateToAutoscale/action |
| Other | Migrate MongoDB database offer to to manual throughput | Migrate MongoDB database offer to to manual throughput. | Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/mongodbDatabases/throughputSettings/migrateToManualThroughput/action |
| Other | Redistribute throughput for the specified physical partitions of the MongoDB database. | Redistribute throughput for the specified physical partitions of the MongoDB database | Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/mongodbDatabases/throughputSettings/redistributeThroughput/action |
| Other | Retrieve throughput for the specified physical partitions of the MongoDB database. | Retrieve throughput for the specified physical partitions of the MongoDB database. | Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/mongodbDatabases/throughputSettings/retrieveThroughput/action |
| Read | Read operation results | Read status of the asynchronous operation. | Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/mongodbDatabases/throughputSettings/migrateToAutoscale/operationResults/read |
| Read | Read operation results | Read status of the asynchronous operation. | Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/mongodbDatabases/throughputSettings/migrateToManualThroughput/operationResults/read |
| Read | Read operation results | Read status of the asynchronous operation. | Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/mongodbDatabases/throughputSettings/operationResults/read |
3. Summary of granted access per role
The below table summarize which access is granted with which role
| Role definition | Access granted |
|---|---|
| Built-in role Cosmos DB Account Reader Role | Read access on Cosmos DB account. Can retrieve read-only key |
| Custom role Dbaas-Nosql-GetKeys | In addition to Cosmos DB Account Reader Role, grant acces to write keys only |
| Custom role Dbaas-nosql-MongoDBWrite | In addition to Cosmos DB Account Reader Role and Custom role Dbaas-Nosql-GetKeys, grant acces to write keys and to write operations from embedded Data explorer |
DBaas Opensearch
Multi tenancy
Opensearch-dashoard implements the concept of multi tenancy to make the consultation of data and dashboards confidential.
Tenant:
Tenants in opensearch-dashboard are spaces for saving index patterns, visualizations, dashboards, and other opensearch-dashboard objects. By default, all opensearch-dashboard users have access to two tenants: Private and Global. The global tenant is shared between every opensearch-dashboard user. The private tenant is exclusive to each user and can’t be shared.
Tenants are useful for safely sharing your work with other opensearch-dashboard users. You can control which roles have access to a tenant and whether those roles have read or write access.
You might use the private tenant for exploratory work, create detailed visualizations with your team in an analysts tenant, and maintain a summary dashboard for corporate leadership in an executive tenant.
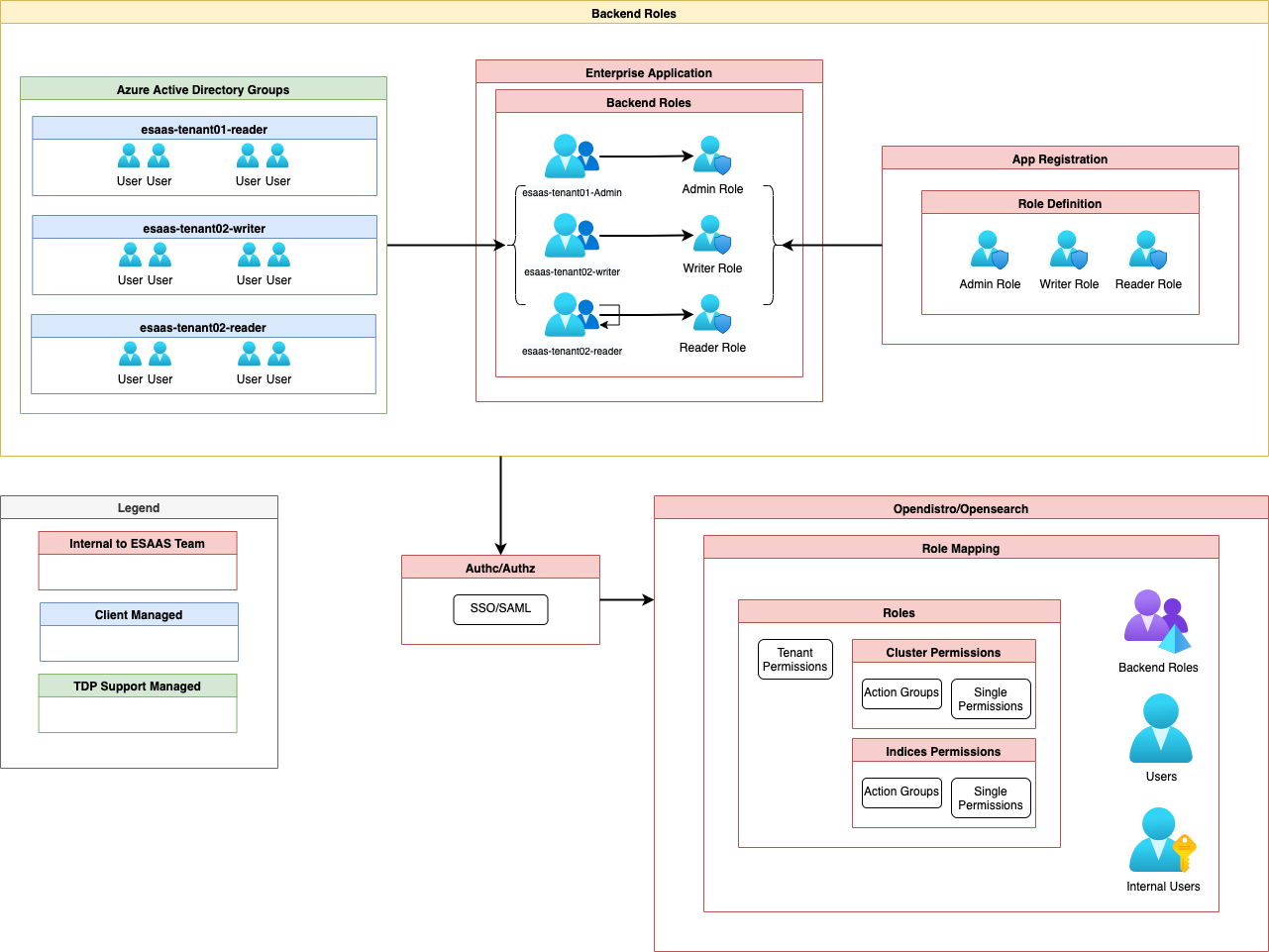
Use cases:
- Provide dedicated opensearch-dashboard accesses to different team in the same entity or company
- Isolate the access between several elasticsearch indices
Warning::: we do not recommend using this multi tenancy feature to isolate high confidential information. Depending on the context, we recommend to use dedicated clusters to have a strong logical segregation between the data of multiple clusters. :::
What to do ?
By default, DBaas opensearch is provided with a single tenant (with the name of your instance). All the provided users have access to this default tenant.
To set up the multi tenancy feature, you first need to define the following information:
| Tenant Name | Index pattern to query | List of users |
|---|---|---|
| tenantA | tenanta-* | user1, user2 etc... |
Note 1: please be careful on the "index pattern to query" section. If there is an overlap, 2 tenants could have access to the same data, that could lead to a data leakage. Note 2: You should think first of what you want, second adapt the index where the data is stored and finally, define the tenant.
Once done, raise a ticket to support-platform@thalesdigital.io asking for an escalation to tdp-esaas, with the owner of the service (on your business line side) with the following data:
- name of your cluster
- tenancy definition (table below)
Give access to DBaas opensearch
Look at the dedicated doc opensearch-rbac